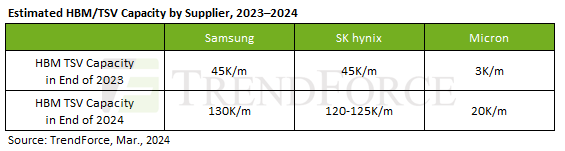
By the end of 2024, the DRAM industry is expected to have allocated approximately 250K/m (14%) of total capacity to producing HBM TSV, with an estimated annual supply bit growth of around 260%, says TrendForce svp Avril Wu.
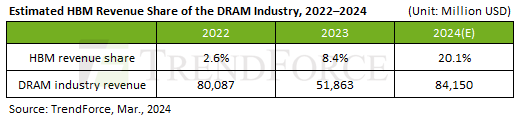
HBM’s revenue share within the DRAM industry—around 8.4% in 2023—is projected to increase to 20.1% by the end of 2024.
The die size of HBM is generally 35–45% larger than DDR5 of the same process and capacity (for example, 24Gb compared to 24Gb).
The yield rate (including TSV packaging) for HBM is approximately 20–30% lower than that of DDR5, and the production cycle (including TSV) is 1.5 to 2 months longer than DDR5.
HBM has a longer production cycle than DDR5 – over two quarters from wafer start to final packaging.
Samsung’s total HBM capacity is expected to reach around 130K (including TSV) by year-end; Hynix’s capacity is around 120K.
Stay up to date with the latest in industry offers by subscribing us. Our newsletter is your key to receiving expert tips.

hina's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) has issued a rare monitoring report warning that rising memory prices are spreading across the electronics supply chain as tight supply and

Nvidia strengthened its dominance in the add-in-board (AIB) GPU market in the fourth quarter of 2025, capturing a record 94% market share even as overall shipments dipped amid rising memory prices and

Broadcom shares rose sharply in aftermarket trade on Wednesday after the artificial intelligence chips maker delivered a quarterly top and bottom-line beat and provided current quarter revenue guidanc